|
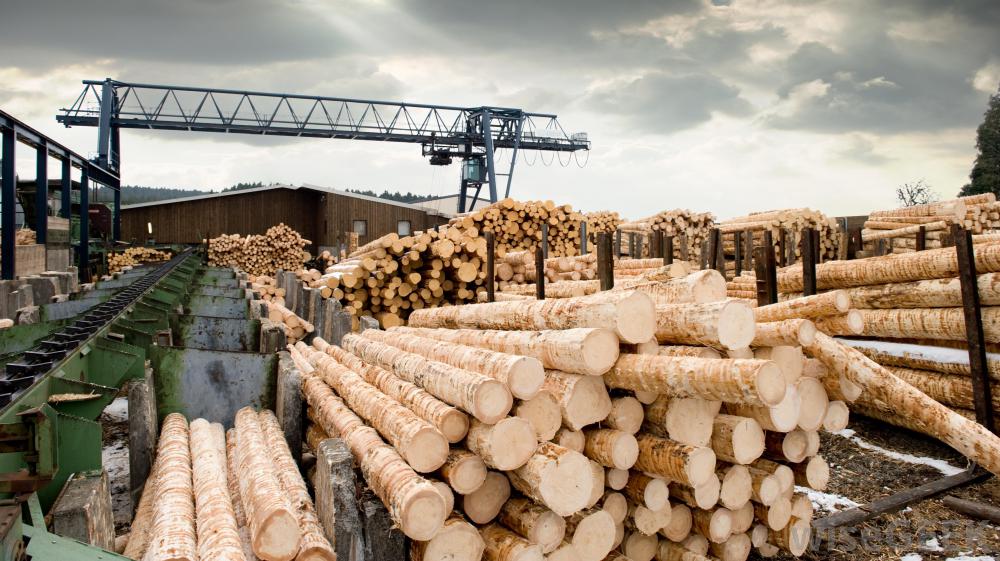
Step 1 - Logging & Transportation – Timber harvesting, or logging, is the first step to getting a log to the sawmill. Trees are cut down using chainsaws during the logging process. This step is known as felling. Felling is essentially cutting down the tree and cutting it to length. Then, the log is delimbed and loaded on a truck for transportation to the mill. Once at the mill, the logs are unloaded and stacked into piles where they wait to be cut.
Step 2 – The Log Enters the Sawmill – The log is moved using a piece of heavy machinery and put on a belt where it awaits to be cut. Step 3 – Debarking the Log – Once the log gets to the front of the conveyor belt, it will enter the mill to be debarked. A debarking machine is used to strip the log of its bark. Most sawmills use debarking machines like mechanical ring cutters, cambio drums, or water-jet blasters. Logs are also bucked or crosscut with a circular saw into specific lengths at this stage. The bark is then saved as it can be sold as mulch or used to fuel certain kilns at a sawmill. Step 4 – Metal Detection – Each log will go through a large metal detector before being cut. Since trees can live for hundreds of years, there’s no saying what could be found in them. Often you will find nails, wire fencing, or other metals in the logs which can ruin your sawmill blades if they’re not caught beforehand. For the logs to have metal in them, the metal will either be removed, or the log will be cut into smaller sections so as much as possible can be salvaged. Step 5 – Merchandising the Log – Makes sawmills much more efficient. Lasers scanning or camera viewing estimates the raw log for its maximum cut value. This information determines what sizes of timber, dimensional lumber, and boards can come from a particular log. Merchandising takes in more than just the log’s length and girth. It assesses each log for market conditions and standing orders. Step 6 – Head Rig Sawing – “The heart of the sawmill” - Logs enter the head rig saw by getting clamped on a conveyor belt where the head rig blades move through the log. Step 7 – Canting – The head rig cuts the log into sections called cants. The first or primary breakdown is called the best opening face (BOF). This sets a flat surface to square the work for secondary cants that turn into rough sizes for finished lumber products. Waste sections, or slabs, from cants are recycled into chips, pellets, or mulch. Step 8 – Resawing – Cants that enter the resawing stage are usually being milled into rough cut lumber. The resaw uses multiple bandsaw or gang saw blades to cut the log into the boards that were merchandised. Step 9 – Edging the Log – The lumber gets its sides cut. This squares up the log so that it fits a specific grade or width. Step 10 – Trimming – The trimmer is used to cut the lumber to length. The length will vary based on the order or lumber size. Step 11 – Grading the Lumber – The actual milling process is now complete. The lumber is ready to be graded. This is essentially a process for quality control. Since most sawmills won’t plane lumber and only sell rough cut, the grade is usually known as “FAS”. Step 12 – Drying – Many sawmills don’t use a kiln and will just let their lumber air dry. Others buy kilns which can speed up the drying process significantly and increase the value of the lumber. Most commercial sawmills specialize in processing either softwoods or hardwoods. A few sawmills tool up for both tree types, but that’s not common. The residential and light commercial construction industries primarily use softwood lumber for framing and rough carpentry. Hardwood materials are used for furniture and finished products, including flooring, staircases, and plywood veneer panels. Three main lumber products come from a sawmill production line. - Timbers – large-cut - end-products >5” thick – beams and posts - Dimensional – most common – 2-5” thick and 2-12” wide – plate, joist, stud, header, and rafter - Boards – Thin cuts – ¾-1” thick – 2-12” wide – sheathing, planking, pallets, crates, furniture frames Specialized shapes – interlocking tongue and groove, shiplap edges, rounding profiles Sawmills require power for other reasons besides turning blades and running conveyors. They need electrical power to operate advanced computerized systems for optimizing cuts, Programmable Controllers, Human Machine Interfaces, Variable Frequency Drives, Motors, etc. There are roughly 500 lumber manufacturing facilities in the USA. Oregon constitutes 16% of the nations’ softwoods followed by Washington, Georgia, Alabama, California, Arkansas, Mississippi, Idaho, North Carolina, and Texas. The top four largest softwood sawmill companies are: Weyerhaeuser, Georgia-Pacific, West Fraser, and Sierra Pacific. A cant is a sawn log that is sent to another machine for additional processing or sold as a large slab to be used as a building log Sawmill workers have many titles: sawing machine setters, operators, tenders, sawyers, lumber mill workers, timber mill workers, sawmill yard workers, wood machinists, or wood processing workers. The first log cut above the stump is called a butt log or butt cut. Butt off refers to cutting a piece of a log due to a defect. Most of a tree’s value is in the butt log. A stack of lumber is a charge, which refers to a stack that has been processed in a dry kiln. If not dried in a kiln it is simply called a stack. Quantum Automation is proud to provide a massive array of AutomationDirect Safety Products
Fabs = Factory – typical fab will have several hundred equipment items – usually > $2Billion
Clean Rooms = Controls Temperature, Humidity, Dust, damped for Vibration – High purity Air Tools = Machines – Steppers for photolithography, etching, cleaning, doping, and dicing Wafers = Produce ICs - 2014 the 300mm arrived and in 2020 the new 450mm – roughly 18” diameter PCBs = Printed Circuit Boards SMT = Surface Mount Technology for Single or Multi-Layer PCBs ICs = Integrated Circuits are used for all below to go on PCBs CPU – Central Processing Unit – wires through the PCB to everything below RAM – Random Access Memory SSD – Solid State Drives HD – Hard Disk IO – Input Output Devices
Wafers – How to make
Major Fabs – SMIC, Micron, Intel, Apple, Analog Devices, Tower Jazz, Samsung, Texas Instruments, TSMC, UMC, ST Microelectronics Major Tools – Teradyne, Advantest, Applied Materials, LAM Research, KLA, ASML Gas Delivery Equipment – Separated Ducts and Piping for Air and Liquid Wet Benches – ICs get dipped into chemical tanks Wafer Boats – transport Wafers in process to other tools Regenerative Oxidizers – Cleans Effluent Air Scrubbers – Cleans Effluent Liquids Environmental – LandfillsPrimary Treatment – Flare Stations Secondary Treatment - Methane Cogeneration Advanced Treatment - High BTU Cogeneration
Stalled Pneumatic Pumps - Minimize the amount of Methane Gas that is released to the atmosphere (help reduce odor & smog) - Maximize the amount of Methane Gas you can use to fuel the landfill Cogeneration Plant - QBumpBox and QSolarBumpBox fixes your stalled pneumatic pumps (see brochure) Stormwater Basins - Meet CA Regulation for Water Conditioning – Phase II MS4 Permits - Off Grid Cloud Based Stormwater Dosing Skids (see attached article) - Attached also is California Water Board’s Fact Sheet (other states have similar plans) NPDES - National Pollutant Discharge Elimination Systems CROMERR - Cross-Media Electronic Reporting Rule SMARTS - Stormwater Multiple Application and Report Tracking System ERA – Exceedance Response Action BMP – Best Management Practices NAL – Numeric Action Level SWPPP – Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan Level 2 ERA Action Plan – Intermediate Tote Treatment – Flocculant & Aeration Systems
Power Generation
Substation Management – IEC 61850-3
QSolarBattery
ITS – Intelligent Transportation Systems– Signage – Urban (local power) and Rural (requires QSolarBattery) for Remote Monitoring and Control – Toll Stations – Industrial – Embedded Computers, Routers with VPN and Fiber Optic, Managed Ethernet switches with Single or Multimode Fiberoptic, NPort Serial to Ethernet Devices, MGate for Protocol Converters – Street Lights & Security Cameras – PoE Managed Switches with Single or Multimode Fiber Optic – Train Signal Crossing – Managed Ethernet Switches and Routers – Tunnel ITS – All of the above plus Fan Control – See Caldecott Tunnel White Paper Stormwater Control– Bridge Underpass Pump House Control + Weather Station + VPN access – Tunnel Drainage Systems – same as above Heavy EquipmentRequires wide temperature rating + higher shock and vibration specifications – Remote Monitoring – QRTU using PLC – LTE Cellular Edge Gateway – Asset Tracking – QRTU – GPS using Embedded Linux Computer with GPS and LTE Cellular New or Recycled Pavement Remote Testing of Pavement – on a pickup truck following the “Smart Paver” by about ¼ mile Benefits – can send the tested sample information directly to the customer and DoT for approval right on the spot vs being sent to a test center. Also, this SQC (Statistical Quality Control Information) can be sent via LTE Cellular to the “Smart Paver” PLC to modify the Setpoint of usually Oil or Water to provide better consistency…therefore Statistical Process Control. – QSolarBattery – Lithium-Ion Battery with possible small Solar Panel for remote power vs a generator to control the Test Machine which requires power to the control panel, servo motor, and compactor. – QRTU – The actual control panel for the Compactor Test Machine
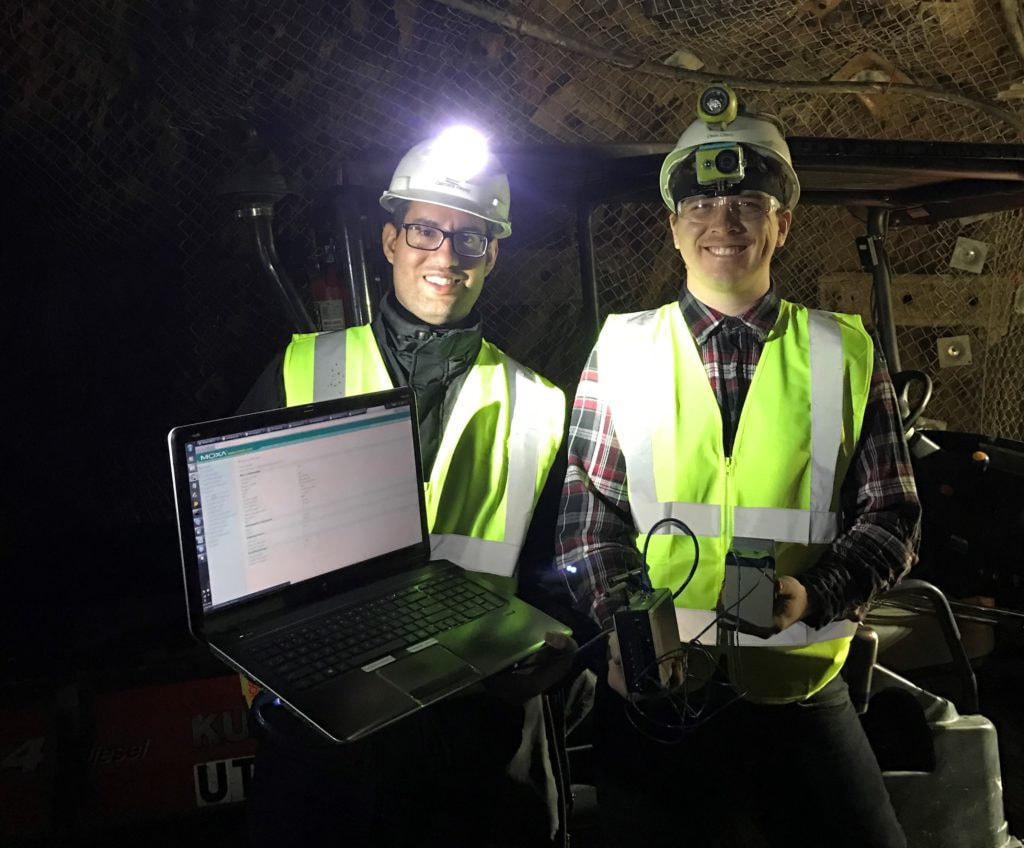
Open Pit Mining Dump Trucks – Like the Belaz 75710 that has (2) 2300HP Diesel Engines or the Liebherr T284 with 4023HP. Use the new MC-1200 IIoT Industrial Moxa Computers (3-year warranty) with i7 processors, built-in Wi-Fi, LTE Cellular, GPS, and mSATA using our QCS IIoT solution with wide temperature (-40 to +70 deg C), high shock (IEC 60068-2-27), and vibration specifications. Record Data either on-board the computer and offload data once out of the pit and back in the service yard using on- board WIFI client and antenna or straight to the cloud at our servers located at AWS. A big truck, Big payloads, Bigger potential problems. Monitor and Data Log Tons/hour, Hours of Operation, Weight of each payload, how many dumps, how many miles driven per shift. Use analytics to determine wear and tear and do preventative maintenance for higher Availability. We can turn-key the project for you.
On a ship there are many parameters that need to be controlled or monitored including: – Temperatures, Pressure, Level, Viscosity, Flow Control, Position of Vessel, Speed, Torque Control, Voltage, Current, Machinery Status (on/off), and equipment status (open/closed) Propulsion (Main Engine) and Power (Auxiliary Engines) Monitoring & Control – Fuel Consumption, combustion temperature, engine temperature, diesel engine safety and start/up, generator voltage and frequency control, generator load in KW and %, load control, torque, heavy consumers logic, control of diesel-electric propulsion, thrusters monitoring, and control, etc. Auxiliary Machinery Monitoring and Control – Main sea & fresh-water cooling system – pumps, system pressure, temp, etc. – Potable and fresh-water control, Air Compressors, Bilge & Sludge – tank level, pumps, fuel oil system – Tank levels, temperature, viscosity, flow, purifiers, heaters, etc. – Other cooling systems – Boiler/steam system – pumps, valves, pressure temperature, etc. – Air Conditioning – Ballast water treatment – Exhaust gas treatment equipment Cargo & Ballast Monitoring & Control – For safe on and offloading of cargo, especially on tankers, this process is closely monitored, and many times incorporates functions like level gauging, control of cargo pumps, valve control, ballast ballast pump control, heeling control, remote monitoring of temperature, pressure, and flow, possibly humidity control. Condition-based Monitoring – monitor equipment – feed main control and monitoring system and/or IIoT – preventative maintenance Industry Solutions
Automation Projects – Machines
– Turn-Key Assembly Lines – Robotic Assembly with Vision Systems for Validation – Clean Room Systems – Aseptic Design – Sterilizers – Incineration of Bio-Waste – Material Handling Systems – Continuous Specimen Sorting Systems – Packing Line Integration These machines use many different types of Control and Networking Types – Discrete Control – Assembly – Packaging – Material Handling – Barcoding – RFID – Batch Control – Recipe Control – Fermentation – Continuous Process Control – Chemical Plants – Motion Control – Robotics – Vision Systems – Validation – Networking – In plant or in Hospital Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Pharmaceutical Products – Bottle Handling – Filling and Capping – Vial Filling – Dispensing & Coating – Soft Gel Machines – Dryers – Container & Bag Filling – Inspection – Packaging Medical Products – Laboratory Equipment for Research & Development – Syringe Assembly, Filling, and Plunger Insertion – Precise Drop Dispenser – PinTool Dispenser – Storage Systems for Cuvettes, Vials, Bottles, Tablets, Liquid Tanks – Medical Device Assembly Machines – like valves and Instruments – Dispensing Machines with Pumps for Blood, Plasma, Liquid Drugs in Pouches – Fermentation Process – Growing Organisms to create certain drugs – X-Ray, MRI, Cat-Scan, etc. machines
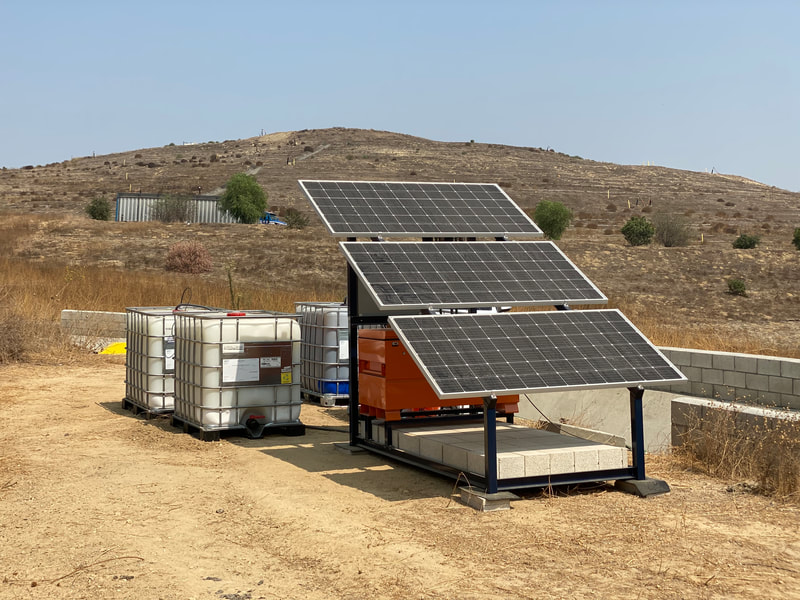
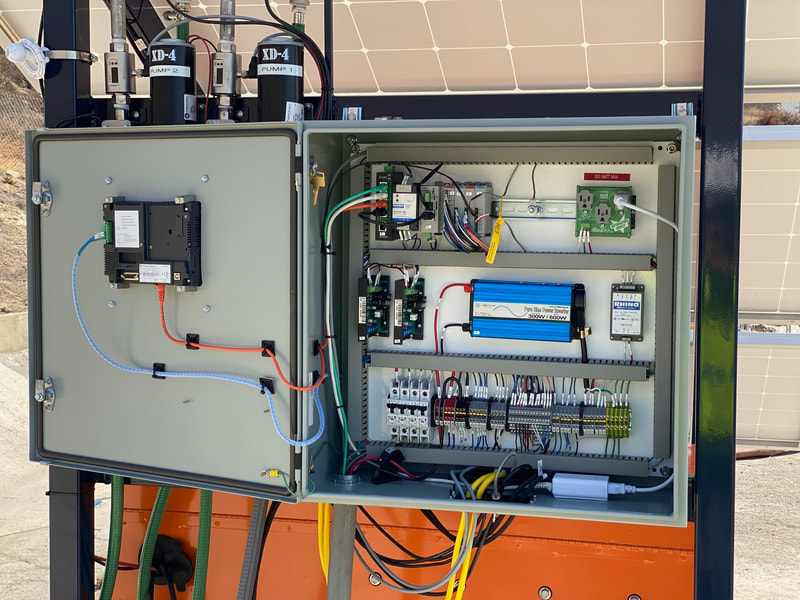
Solution for Smart Farming = QSolarBattery + QRTU
QSolarBatteryProvides Off-Grid Power to the QRTU for hard to reach rural places Success StoriesBale Hay While the Sun Shines: A Revolution in Commercial Hay ProductionA steam generating plant on wheels? That’s right. The DewPoint 6110 hooks up between a large farm tractor and hay balers that make large rectangular bales from 1,500 to 2,000 lb each (Fig. 1). Its purpose is to add moisture to dry hay to prevent mechanical damage to the crop during the baling process. This revolutionary concept, which has been successfully used and refined over the past 14 years, will change the way hay is made. Read more Oil & Gas Production – On-Shore– Oil Rigs, Second Stage Recovery, Fracking, Crude Oil Wells
– All need QRTU, and many need QSolarBattery Oil &Gas Production – Off-Shore – Mostly use full SCADA systems with SATCOM, but QUPS, QSolarBattery, QRTU can all apply. Oil & Gas Pipeline – from Production to Refinery – LACT – Leased Automated Custody Transfer – determines which oil field the crude came from that goes into the pipeline Oil Refining – Distributed Control Systems – Honeywell Experion PKS R.410 – Emergency Shutdown Systems – Schneider Electric – Triconex – Tricon CX – SIL 3 Rated – Rockwell Automation – ICS – Triplex “Trusted” – SIL 3 rated – Scalable Fault-Tolerant Controls System – Quantum Automation – Sell Moxa Industrial Computers, Routers, Switches, M-Gates, N-Ports that are all Rated C1D2/ATEX Zone 2 Tank Farm Automation– Float and Tape – Strapping Tables – Hydrostatic Tank Gauging – Pressure & Temp = Volume – New method using Ultrasonic Sensing Gasoline Pipeline to Truck Terminals or Airport Terminals– Truck Rack Loading Systems, Flow, Level, Volume Marketing – Gasoline Stations– Pumps, Tanks, Level, Flow, Rate Soil Remediation – Gas Station Tank Leak – Clean up – Moxa M-Gates, QRTU, QSolarBattery Fine Chemicals – Cosmetics, Perfumes, Methane, Pharmaceuticals United States has a vast System of collection sewers, pumping stations, and treatment plants. Sewers
collect wastewater from homes, businesses, and many industries, and deliver it to plants for treatment. Most treatment plants are built to clean wastewater for discharge into streams or other receiving waters, or for reuse. Primary Stage – The solids are allowed to settle and be removed from wastewater. – As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. – It then passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom. – Sewage still contains organic and inorganic matter along with other suspended solids. These solids are minute particles that sink to the bottom where they form a mass of solids called raw primary biosolids (sludge) which can be removed from the tanks by pumping. The sludge is used as fertilizer or disposed of in a landfill or incinerated. The Secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. – The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85% of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used are the trickling filter (a bed of stones from 3-6 feet deep through which sewage passes) or (interlocking pieces of corrugated plastic or other synthetic media) which then flows to another sedimentation tank. The trend today is towards the use of the activated sludge process which speeds up the work of the bacteria by bringing air and sludge heavily laden with bacteria into close contact with sewage. It is pumped into an aeration tank, where it is mixed with air and sludge loaded with bacteria and allowed to remain for several hours breaking down the organic matter into harmless by-products (primary effluent, sludge basin, air compressor, clarifier, recycle pump, return sludge, back to clarifier, then secondary effluent, discharge to river or land application) Applications Pumping Systems, Settling Tanks, Aeration Tank, Final Clarifiers, Chlorine Disinfection, Ultraviolet Disinfection, Filtration, Water reuse, Solids Thickening, Digesters, Solids, Dewatering (Belt Presses), Biosolids Recycling, Wastewater Quality Monitoring, Chemical Testing, Chemical Feed Systems, Wastewater Evaporators, Biofiltration Systems, Bioreactor Systems, Skimming Collection Systems. Low-tech solutions: – Aerobic ponds – Shallow, light penetrates to bottom, active algal photosynthesis, Organic matter converted to CO2, NO3, HSO4, HPO4 – Facultative ponds – Pond 1 – 2.5m deep – not easily subject to upsets due to fluctuations in Q, loading – Anaerobic ponds – Primarily used as a pretreatment process for high strength, high temperature wastes. Can handle much higher loadings…Stage 1 – Acid fermentation (Organics – Organic acids). Stage 2 – Methane fermentation Organic Acids to CH4 and CO2. Storing Water
Applications
Cleaning Water
Resources
Grain Plants & Solos
Cereal & Oatmeal
Press, Ovens, Refrigeration Meat, Poultry, Fish
Fruits, Nuts, Vegetables
Pasta & Rice
Candy & Chocolates
Salad Dressing
Dairy
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Orders & Support
714-854-0800 | 7am - 5pm PST
[email protected] | www.QuantumAutomation.com
4400 East La Palma Avenue, Anaheim, CA 92807
714-854-0800 | 7am - 5pm PST
[email protected] | www.QuantumAutomation.com
4400 East La Palma Avenue, Anaheim, CA 92807
|
Copyright © Quantum Automation. All Rights Reserved.
|
Website Development RavingDesignz
|

























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed